Cisco IOS DHCP Server Configuration
.png)
Cisco devices running Cisco programming incorporate Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) servers and transfer specialist programming. The Cisco IOS DHCP server is a full usage server that allocates and oversees IP addresses from determined location pools inside the gadget to DHCP customers. The DHCP server can be arranged to allocate extra parameters, for example, the IP address of the Domain Name System (DNS) server and the default devices. Today, we'll be diving into the DHCP server system to work through the general use case as well as walking through a configuration example for your network.

Overview of the DHCP Server
The Cisco DHCP server acknowledges address task solicitations and restorations from the customer and appoints the addresses from predefined gatherings of addresses inside DHCP address pools. These location pools can likewise be designed to supply extra data to the mentioning customer, for example, the IP address of the Domain Name System (DNS) server, the default gadget, and other setup parameters. The Cisco DHCP server can acknowledge communication from privately joined LAN portions or from DHCP demands that have been sent by other DHCP transfer operators inside the system.
Download the guide and refer back to it at any time!
General Usage Scenarios
There are four key DHCP usage scenarios:
- Initial Client Connection: the client requests from the DHCP server an IP address and other parameter values for accessing network services
- IP Usage Extension: the client contacts the DHCP server to extend the usage of its current IP address
- Client Connection After Reboot: the client contacts the DHCP server for confirmation that it can use the same IP address being used before the reboot
- Client Disconnection: the client requests the DHCP server to release its IP address.
____________
Field Services for Configurations
We offer remote staging and configuration environments to help you get a leg-up on getting your gear ready for deployment. EXTEND Field Services also gives you access to SmartHands engineers to augment your team when you need an extra set of hands.
____________
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
DHCP is an application layer protocol used to distribute various network configuration parameters to devices on a TCP/IP network. – IP addresses, subnet masks, default gateways, DNS servers, etc. DHCP employs a client-server architecture; a DHCP client is configured to request network parameters from a DHCP server on the network. A DHCP server is configured with a pool of available IP addresses and assigns one of them to the DHCP client.
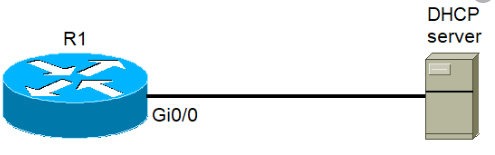
When you're looking to configure DHCP on Cisco routers, Layer 3 and Layer 2 switches, follow these steps:
- Exclude IP addresses from being assigned by DHCP
- Create a new DHCP pool
- Define a subnet that will be used to assign IP addresses to hosts
- Define the default gateway
- Define the DNS server
- Define the DNS domain name
- Define the lease duration by using the lease time
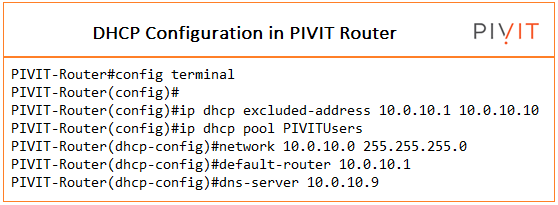
Configuring Manual Bindings
A location restricting is a mapping between the IP address and MAC address of a customer. The IP address of a customer can be relegated physically by an overseer or doled out consequently from a pool by a DHCP server.
Manual ties are IP addresses physically mapped to MAC locations of hosts that are found in the DHCP database. Manual ties are put away in the NVRAM of the DHCP server and are simply extraordinary location pools. There is no restriction to the number of manual ties, however, you can arrange just a single manual restricting per have a pool.
Note We cannot configure manual bindings within the same pool.
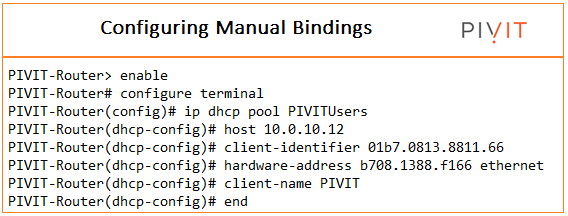
PivIT Troubleshooting Tip
You can determine the client identifier by using the debug IP DHCP server packet command.
PIVIT-Router# debug ip dhcp server packet
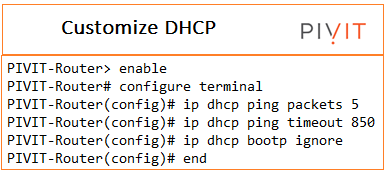
Customizing DHCP Server Operation
By default, the DHCP server pings a pool address twice before assigning a particular address to a requesting client. If the ping is unanswered, the DHCP server assumes (with a high probability) that the address is not in use and assigns the address to the requesting client.
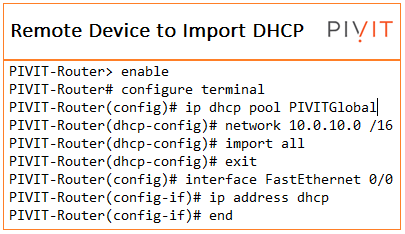
Configuring the Remote Device to Import DHCP Options
Perform the following task to configure the remote device to import DHCP options
DHCP Show Commands
- Show IP DHCP import
- Show IP DHCP Pool
- Show IP DHCP binding
- Show IP DHCP database
- Show IP DHCP server statistics
We hope this configuration guide helped! We created the Tech Corner to connect with you on configuring your DHCP Server, join in product discussions, access configuration guides, share product comparisons, and provide you with information about the industry! Subscribe to the Tech Corner today!
