Configuring Cisco On-Demand Routing (ODR)
ODR is fundamentally pertinent in hub and spoke networks and a spoked arrangement where CDP can be utilized. It isn't alluring to include the overhead of a directing convention like RIP, EIGRP, or OSPF. The primary thought is that the prefixes can be traded from the spoke switches (otherwise called stub switches) to the center point switch. The center point switch can publicize a default course to the spoke switches. Prefixes, by means of ODR, can be redistributed into another direction convention to guarantee full start to finish availability with different pieces of the system.
ODR relies on Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP), so only networks that support CDP can be part of an ODR configuration. This immediately eliminates Frame Relay with point-to-multipoint sub interfaces and other non-broadcast topologies.
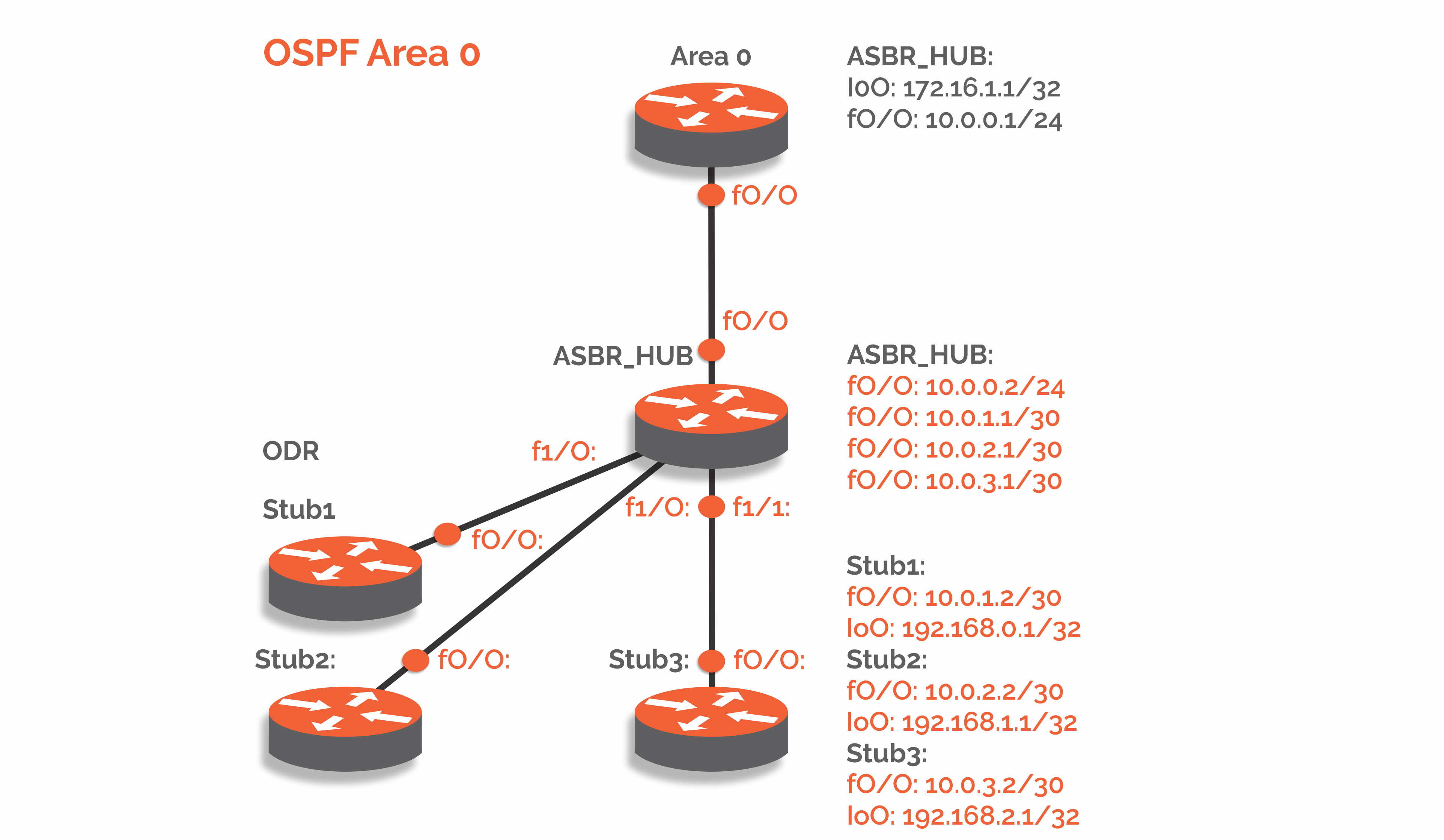
Example with a given topology:
Prerequisites for Configuring On-Demand Routing:
Cisco Discovery Protocol must be enabled.
Benefits of On-Demand Routing
This module describes how to configure On-Demand Routing. The ODR provides IP routing for stub sites, along with minimum cost. The cost of a general, dynamic routing protocol is avoided without configuration and management burden of static routing. The configuration follows:
router ospf 1
log-adjacency-changes
redistribute odr subnets
network 10.0.0.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
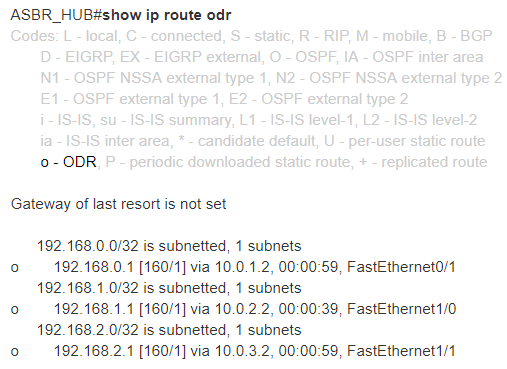
After the network converges and routes are communicated via CDP, we can see the default route advertised via ODR on any spoke router:

On the hub router, we see the networks connected to the spoke routers advertised via CDP and included in the routing table as ODR routes.
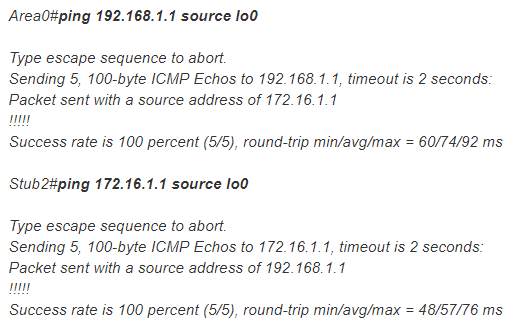
With redistribution into OSPF, we can confirm end-to-end connectivity from the OSPF router and one of the spoke routers:
Lookin for More?
Visit the Tech Corner to find more routing protocols and other resources.
