The Importance of Maintenance Audits — And How to Carry Them Out
%20The%20Importance%20of%20Maintenance%20Audits%20_%E2%80%94%20And%20How%20to%20Carry%20Them%20Out.png)
Reliable IT infrastructure is the backbone of any successful enterprise. Technology enables employees to be productive and creative, orchestrating growth for the company.
But they can’t do that if the equipment they frequently use malfunctions or breaks down. This is where a maintenance audit comes in.
Maintenance is crucial for IT infrastructure, especially hardware, for which many companies rely on external expertise — not every business has a hardware engineer at its disposal. Data centers, in particular, need a solid maintenance strategy because their equipment is operational around the clock.
If your maintenance strategy is falling short of delivering near-perfect uptime and availability of resources, it’s time for a maintenance audit.
In this article, we will discuss the following:
- What an IT maintenance audit is.
- Why maintenance audits are important.
- What strategies you can utilize to help achieve your goals.
Not the article you were looking for today? Try these out:
- Third-Party Maintenance: All Your Questions Explained
- 5 Reasons to Consider a Third-Party Maintenance Provider in 2023
- Why Chip Supply Shortages Could Bring Redesigns, and What It Means
- Here’s Why Transparency Matters for Third-Party Network Maintenance
What Is an IT Maintenance Audit?
A maintenance audit reviews the maintenance of equipment, inventory, and operations. It’s a process of evaluating the maintenance strategy and its implementation of organizational goals. It looks at the processes for maintenance tasks such as repairs or security checks.
An IT maintenance audit aims to find problems and areas of improvement in the maintenance strategy so that you can reduce overall costs and performance can be improved.
Maintenance audits are typically conducted internally. It should be a regular practice, ideally annually or semi-annually.
Why Is a Maintenance Audit Important?
Maintenance is critical to getting the most out of your IT infrastructure. Maintenance audits help fix and improve the maintenance strategy, which, in turn, reaps into the benefits of maintaining assets well. Here’s why it’s so important:
Identify Issues Early On
An IT maintenance audit looks at the state of an enterprise’s maintenance strategy to identify areas that need improvement. It helps companies identify mistakes early on before showing their real impact.
It also allows companies to adopt the best practices and move with the times. They can learn where maintenance lagged and what or who was responsible for it.
Understanding Priorities
A maintenance audit may reveal which parts of the infrastructure are most important and need priority. Similarly, some components or assets may be over-maintained, wasting resources.
With the help of the audit, companies can recognize which assets qualify for more maintenance spending and which ones they can do without.
Cost Savings
The most impactful benefit of a maintenance audit is potential cost savings. Maintenance can consume a significant percentage of IT spending, and companies want to use more of the IT budget to acquire assets and technologies.
An insightful maintenance audit will identify improvements that can result in cost savings. Depending on the size of the infrastructure, even a small change may result in millions in savings. All those savings can then go towards improving infrastructure.
Compliance
A maintenance audit may also directly or indirectly point out non-compliance. For data centers, non-compliance with applicable regulations on data privacy can result in heavy fines and reputational damage.
As maintenance is central to the security of assets that house all the data, it’s crucial to ensure this part of the infrastructure is prioritized and maintained well.
The Right Maintenance Strategy
You should link your IT maintenance strategy with your business strategy. It should form a part of your overall organizational strategy. Contrary to popular opinion, the goal of IT maintenance isn’t just to avert repairs. It also focuses on improving performance through maintenance.
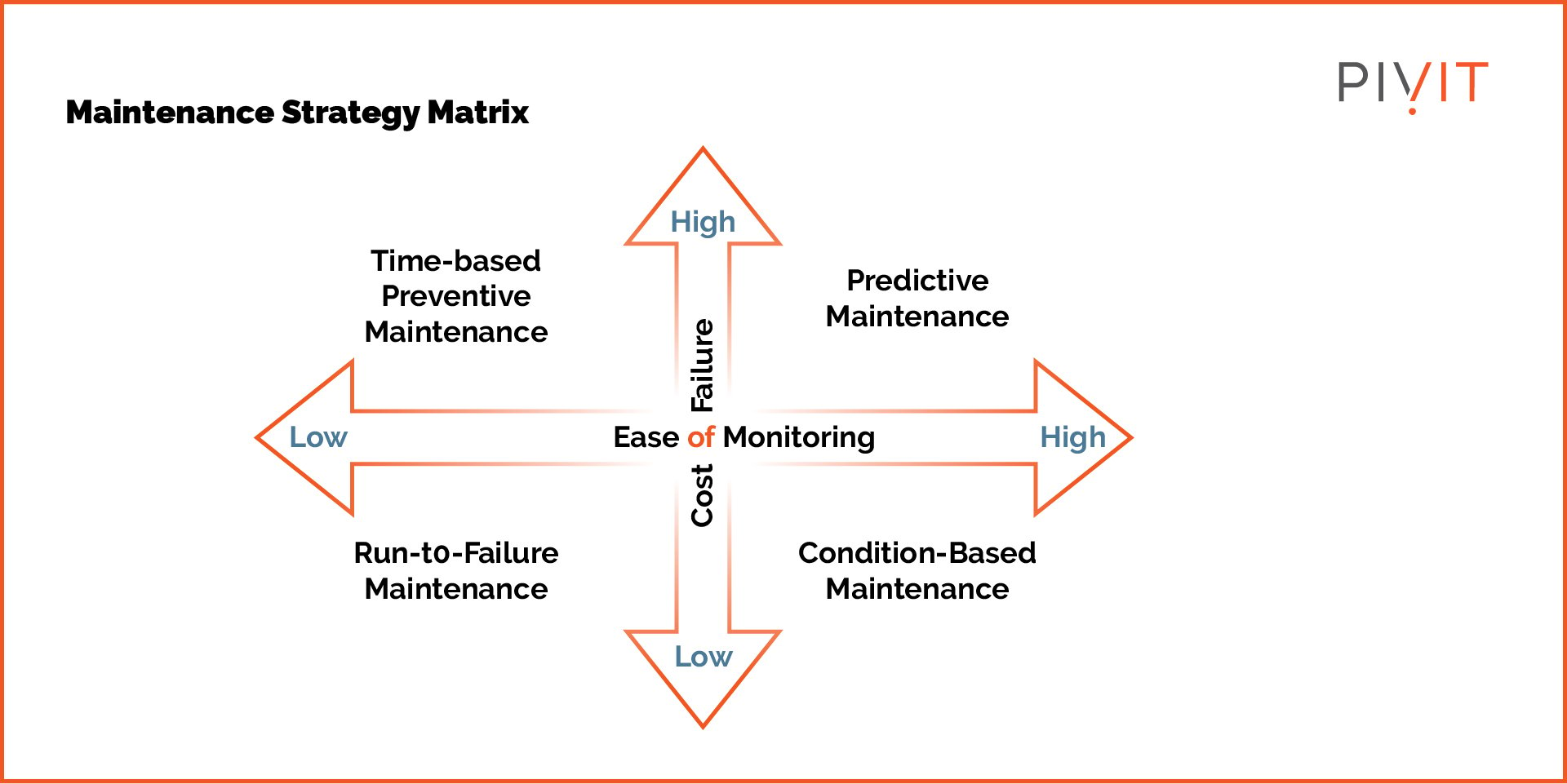
The maintenance strategy should be both preventive and responsive. Repairs and replacements can be reduced, not eliminated. So the strategy needs to outline the measures for preventing failures and the steps to take if hardware fails.
Maintenance strategy may differ by organization, but the following are the three main pillars:
Minimizing Repairs
Your maintenance plan should aim to reduce repairs, as they can be expensive. You can do this through scheduled maintenance, monitoring, and timely replacement.
Of course, you cannot eliminate repairs because the equipment will break down. But you can minimize such instances, especially for critical equipment.
Minimizing Downtime
Downtimes are costly. If hardware or software fails for employees, it results in revenue loss because of productivity loss. Similarly, if downtime occurs for consumers, it results in a loss of revenue.
A good maintenance strategy lays down contingencies for when critical assets fail. Spare equipment is one way to ensure that your infrastructure has high availability and zero downtime.
Maximizing Performance
You want to get the most out of an IT asset’s lifecycle. Therefore, your maintenance strategy should also focus on optimizing equipment performance.
However, you don’t want to be too extreme, as pushing the equipment's lifecycle beyond its capability can also backfire. Recognizing when and in what condition equipment needs replacement is essential.
How to Carry Out a Maintenance Audit?
You should conduct maintenance audits at least once a year. Here are the steps to a comprehensive maintenance audit:
Analyze Documentation
Your maintenance strategy should be well-documented. Reviewing the documentation of the strategy is the first step to determine whether it aligns with the business strategy. It’s important to consider whether any changes in business strategy would impact maintenance.
This step involves reviewing documentation regarding the inventory of assets from different departments and maintenance contracts.
If there’s no official maintenance strategy, the first step would be to develop one.
Measure Against Benchmarks
Benchmarks will help determine if the current maintenance strategy is working or not. For instance, there should be measurable metrics for performance that can be linked with maintenance. These metrics may include repair costs, repair times, outages, downtimes, or cost of maintenance contracts.
Benchmarks should also be revised per the changes in the infrastructure or operations of the company.
If the maintenance falls short of the benchmarks, it’s time to go back to step one and review the strategy documentation.
Gather Feedback
Maintenance audits should also involve the personnel behind maintenance. With the help of interviews or surveys, collect feedback from employees responsible for different maintenance tasks. Ask about issues and how you can improve maintenance procedures.
Feedback from these employees can help improve the maintenance strategy.
Consider Third-Party Maintenance
Maintenance can get complex for data centers and businesses with large, multi-vendor infrastructure environments. In addition, OEM maintenance costs keep increasing yearly in the equipment's lifecycle. You can resolve the problems you may identify in a maintenance audit with the help of a TPM provider.
A TPM provider can take care of maintenance for both new and legacy equipment while reducing the average cost for repair. Most of the responsibility of implementing the maintenance strategy falls on the third party that takes care of the technical side while you and your resources focus on growing the business.
OneCall by PivIT is a reliable maintenance program that has helped many enterprises cut costs and achieve more with their hardware.
With the hybrid maintenance championed by the OneHub dashboard of OneCall, you can manage your maintenance contracts in one place. Furthermore, you can extend the life of your equipment, reducing unnecessary spending.
Consider OneCall to help you exceed those maintenance and performance benchmarks!


