Archive Data Storage Solutions for Optimal Cost Efficiency
%20Your%20Guide%20to%20Data%20Storage%20Archives.png)
Many businesses today produce and store a vast amount of data, much of which needs to be archived. Because of that, archive data storage needs to be efficient yet cost-effective.
The data to be archived isn’t needed at the moment but may be required in the future. So, in essence, it requires a similar level of access and protection compared to data residing on your primary infrastructure, be it on-premise or cloud. Therefore, you must choose the archive storage type according to your specific needs.
In this article, we will discuss the following:
- Various approaches to data storage archives.
- Various approaches to media types.
- How you should choose a solution for your archives.
Not the article you were looking for today? Try these out:
- Dependable, Scalable Solutions for Growing Data Demands
- Data Center Relocation: Challenges and Best Practices
- 3 Things to Consider Before Opting for OEM Storage Maintenance
Understanding Archive Data Storage
We’ve come a long way in data storage technology, from AI-powered self-defending to eco-friendly all-flash solutions. However, when it comes to archiving, you don’t necessarily need all the bells and whistles that will eventually increase the cost per gigabyte. As archives can be enormous in volume, you want an economical solution.
That said, preservation and accessibility are also important factors to consider. The data would only be helpful if you can access it. Similarly, it’s only beneficial if it’s not corrupted.
More importantly, your route for data storage archive depends on your technical capabilities, especially on-site storage, where you’re responsible for the infrastructure.
Common Approaches to Data Storage Archive
Generally, there are three archive data storage approaches, each with unique benefits and drawbacks. Let’s explore each of them:
Batch Archive
This is the most commonly used data archive storage approach, as it’s easier to deploy and not expensive, especially when paired with cheap media. With this approach, data is stored in collections or batches along with metadata that helps identify and locate the data.
Metadata for batches may include project name, creator name, timeframe, etc. However, it doesn’t contain the details of the server the data originally resided on. In other words, the metadata is less detailed than what you would find in a typical backup.
The batch archive approach is helpful for data preservation when data needs to be stored for a long duration.
Hierarchical Storage Management Archive
Hierarchical storage management (HSM) is a tier-based approach that automatically manages and moves data based on policy. Typically, this approach involves high-cost and low-cost storage media, and data automatically moves from the former to the latter based on policy.
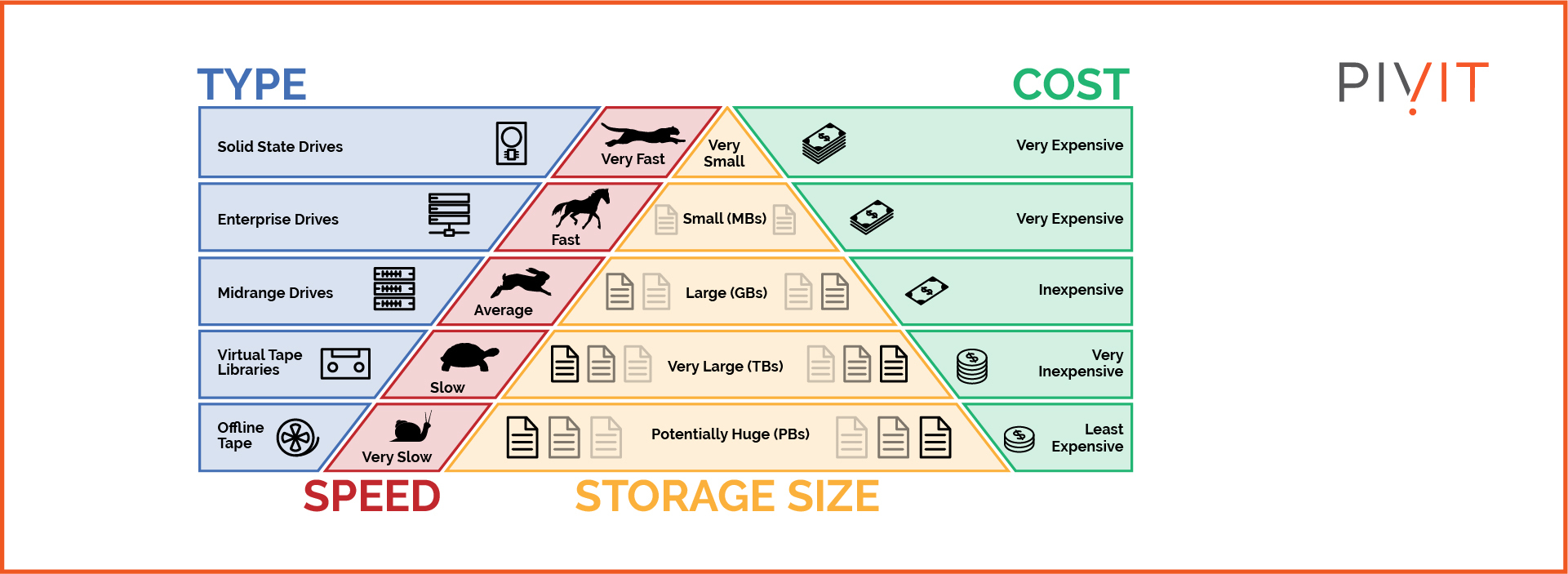
(Data: source)
For instance, data reaching a certain age may be automatically moved to the low-cost storage tier. In other words, this data will be archived.
High-speed storage devices such as solid-state drives (SSD), typically more expensive, are reserved for primary data. On the other hand, data that are no longer needed daily is moved to slow-speed storage devices.
Usually, the archived data leaves a pointer or stub that can be later used to retrieve the archived data.
Real-Time Archive
Real-time archives are created in real-time from the production environment. As data is created, it’s simultaneously archived as well. This approach is typically used for compliance or auditing purposes, where all data has to be stored for a certain period.
It’s similar to a backup, and, in many cases, the archives are immutable. However, the drawback is that such archives don’t necessarily free up space on primary servers or storage unless data is actively removed from there, which may not be the case until the data is no longer needed frequently.
Media Types for Data Archives
Arguably, the most crucial decision is choosing the media type for your data archives. Here are the standard options:
Disk/Removable Disk
A preferred choice for many enterprises, disk storage offers the cost-effectiveness necessary for archiving. Hard drives also offer high capacity, up to terabytes, that can be feasible for storing large volumes of data.
Accessibility is another advantage of disk-based archives. As it’s random access, data can be written anywhere on the disk. Moreover, the RAID technology prevents failure, making them highly reliable.
Similarly, a removable disk also presents a viable option, especially for archives that may be required to move to another site.
The drawback of this media is that it’s not space-efficient in terms of physical space. You’ll need more floor space to house all the disks. As your archives grow, the space needed to accommodate disks will also increase. Moreover, disks are not the most efficient when duplicating data to another site.
Tape
Although tapes were retired from data storage years ago, they continue to be used for archives. Recently, the use of tape for backups and archives has seen a resurgence, particularly due to the rise in ransomware attacks. Archives stored on tape off-site make access impossible for attackers, offering reliable protection for sensitive data.
Moreover, tapes offer an excellent cost-to-capacity ratio, making it an affordable option for storing large amounts of data. Unlike disks, tapes don’t consume a lot of floor space. As mentioned, they can be moved off-site easily, essentially just physically moving them.
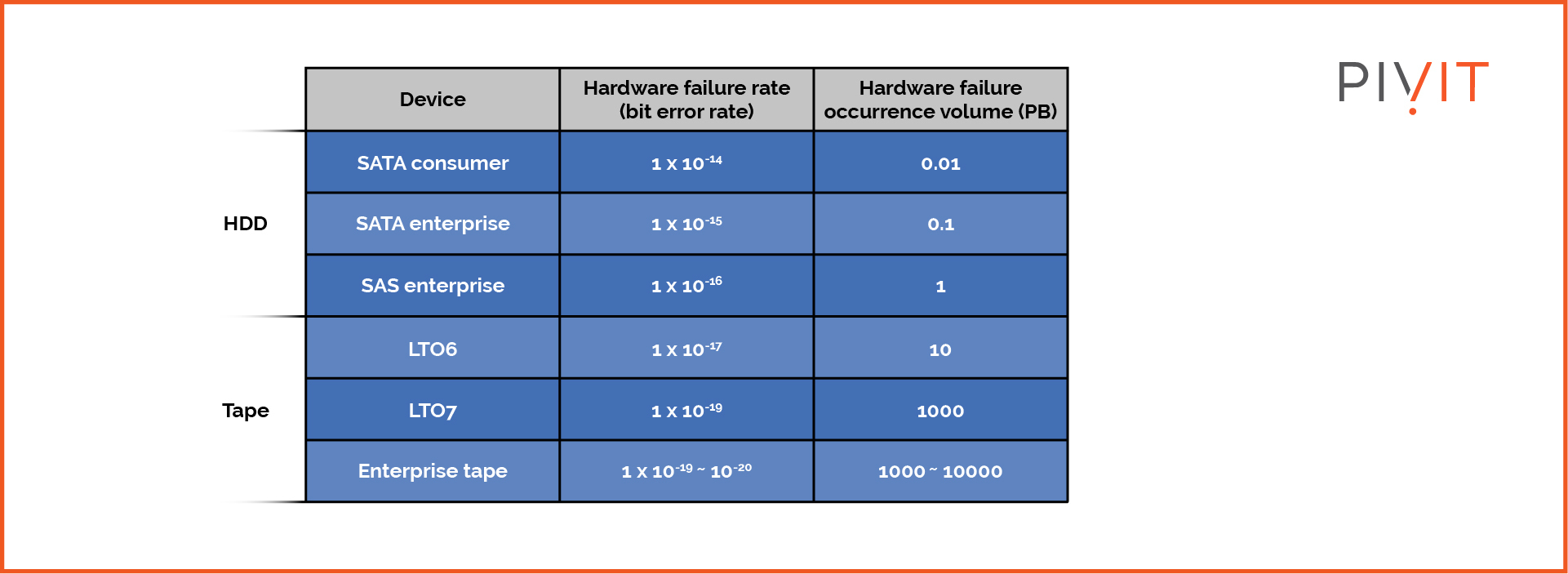
(Data: source)
The only downside is that access can be time-consuming, as tape reads and writes data sequentially.
Flash-Based Storage
Flash storage is having its moment, especially for its performance and efficiency in supporting artificial intelligence (AI) applications. Vendors are adding all sorts of advanced features to their flash offerings. For instance, Dell has revamped its PowerStore lineup with security features and DevOps capabilities.
Flash is another option for data archiving, albeit an expensive one. Although costs for all-flash storage have reduced over the years, it’s not the most cost-effective option compared to cheaper choices like tape or disk.
Cloud Archives
Cloud archive, also termed cold storage, is another viable option for archiving data for long-term retention. It’s a suitable choice for enterprises that may not have the capacity to house the infrastructure for archives on-premise.
Data you won’t need anytime soon can be stored on the cloud. The prices for cloud archives are comparable with other cheap media types and, at times, even lower. Hyperscalers like Amazon and Google offer archive storage services for enterprises.
Things to Consider When Archiving Data
Before choosing the media for your archive data storage, consider the following:
- Data Security: Prioritize solutions that offer robust encryption and reliable access controls, especially when archiving sensitive information. Ensure you comply with applicable data usage, storage, and archive regulations.
- Accessibility and Retrieval: Consider the probability of retrieval and access when choosing a solution and how quick it must be. If the data may be required frequently and speedily, you may need to invest in a more efficient solution, which may be costly.
- Budget: Consider the overall cost of storing data archives and any potential egress fees (when using the cloud). Ensure the technology you select aligns with your budget.
- Redundancy: Does the archive storage offer some level of redundancy? This is necessary for protection against complete data loss or corruption.
Procuring the Best Storage Infrastructure
Every enterprise’s data needs are unique, which should be considered when archiving files and raw data. Your archive data storage infrastructure must be reliable and cost-effective, as you don’t want to spend a lot of money on archives when that money can be used to modernize and improve primary storage.
Disk, tape, and optical storage are all good options. And PivIT can procure all the equipment you need to set up on- or off-site archives.
With an expansive selection of models and providers, PivIT has a full portfolio of storage hardware—with prices that help minimize your expense while meeting lead times you can't beat. All our storage is backed by our lifetime warranty.
When it comes down to the perfect mix of your budget, processor requirements, throughput needs, and access to hands-off support, PivIT is here so you can reach your goals.
